Beautiful Info About What Is A Controller Used For

Understanding DJI Flight Controllers A Comprehensive Guide Drone Nastle
Decoding the Controller
1. Understanding the Role of Controllers in Various Systems
Ever wondered what that thing in your hand actually does? Whether it's a game controller, a thermostat dial, or even the steering wheel in your car, it's all a controller doing its job. A controller, at its heart, is an interface. It's how you tell a system what to do. It's the bridge between your intentions and the system's actions. Think of it like a translator, converting your commands into a language the machine understands.
So, what exactly is a controller? Well, the keyword here is "control" (surprise!). It's about exerting influence, guiding, and directing something. The controller is the tool that facilitates this control. Now, the specifics can get pretty diverse depending on the application. We're not just talking about joysticks here; a simple light switch is, in fact, a basic type of controller. It controls the flow of electricity to a light bulb.
Different types of controllers abound, each tailored for specific tasks. A video game controller is designed for nuanced and rapid input, perfect for navigating virtual worlds and battling digital foes. An industrial controller, on the other hand, might oversee complex processes in a factory, ensuring precise measurements and automated actions. It's like comparing a race car driver's steering wheel to the autopilot system on an airplane — both are controllers, but their functionalities are vastly different!
Ultimately, a controller allows us to interact with complex systems in a manageable way. Without controllers, we'd be left fumbling with raw code or directly manipulating intricate machinery. Imagine trying to play your favorite video game by directly rewriting the game's memory! No thanks, I'll stick to the controller, thank you very much.

The Many Faces of Control
2. Exploring Diverse Applications of Controllers
Let's dive a bit deeper into the sheer variety of controllers we encounter in our daily lives. Obviously, gaming controllers are a big one. These evolved from simple joysticks and buttons to complex devices with pressure-sensitive triggers, motion sensors, and even built-in microphones. They're designed for incredibly precise and responsive control, allowing players to immerse themselves in virtual worlds.
Beyond gaming, controllers are ubiquitous in the realm of home appliances. Your television remote is a controller. Your air conditioner's thermostat? Controller. Even the volume knob on your old stereo is a controller! These devices give you command over your environment, letting you adjust settings and personalize your experience.
In the industrial world, controllers are absolutely critical. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are the brains behind countless automated processes. They monitor sensors, analyze data, and execute commands to control everything from assembly lines to chemical reactions. These controllers are essential for efficiency, precision, and safety in modern manufacturing.
And don't forget about vehicles! Cars, airplanes, boats — they all rely heavily on controllers. Steering wheels, throttles, rudders, and even the cruise control system are all examples of controllers that allow us to navigate and manage these complex machines. The evolution of vehicle control systems has been nothing short of remarkable, and continues to advance with self-driving technology.

Logitech Controller Was Used To Steer The Titan Joburg ETC
The Inner Workings
3. Delving into the Technical Aspects of Controller Functionality
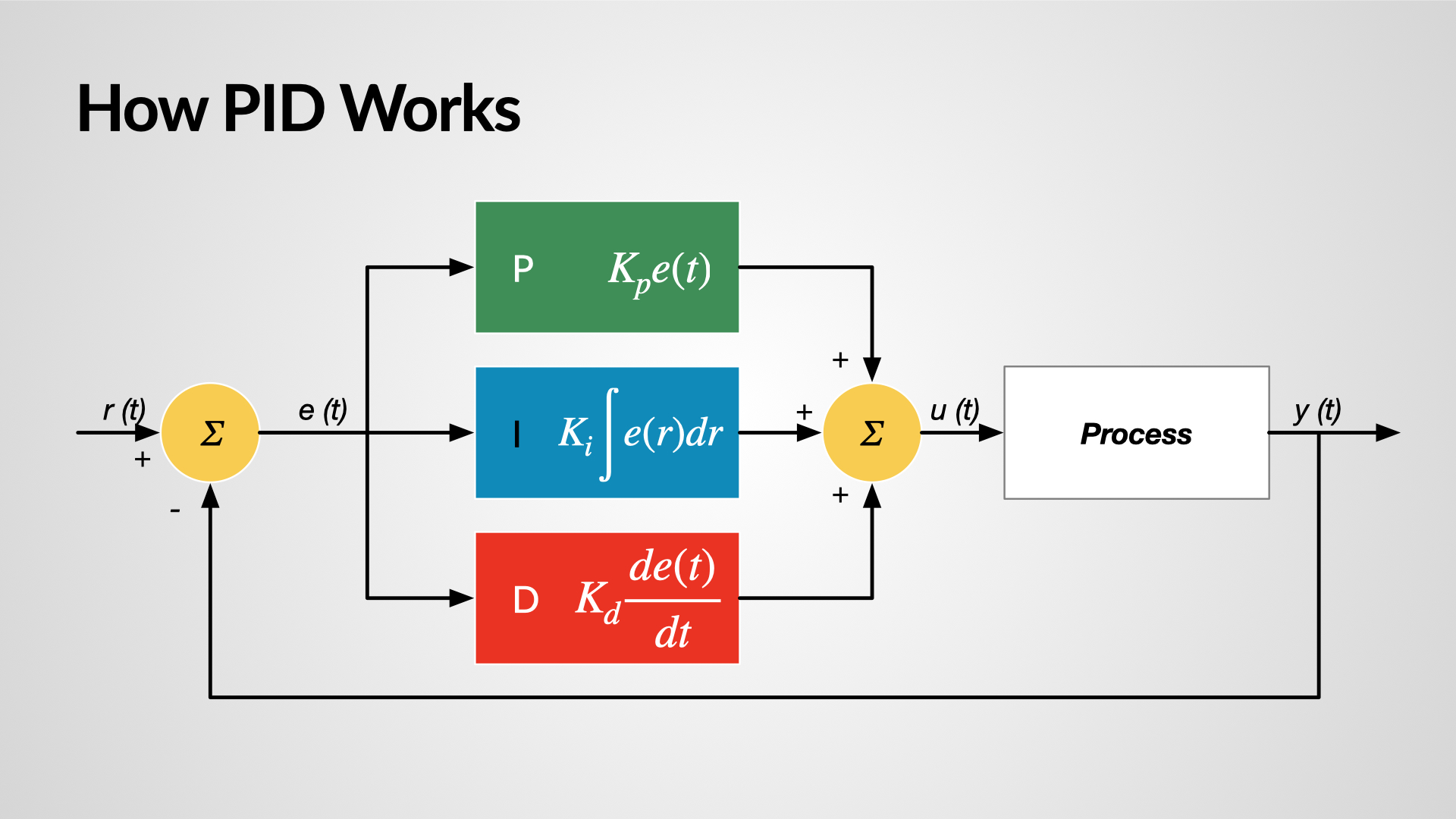
Okay, so we know what controllers do, but how do they actually do it? The answer, as with most things tech-related, depends on the specific type of controller. However, there are some fundamental principles that apply across the board. At the most basic level, a controller receives input from the user (e.g., button press, dial turn, voice command), and then translates that input into a signal that the controlled system can understand.
In many cases, this translation involves converting physical actions into electrical signals. For example, when you press a button on a game controller, it closes a circuit, sending an electrical signal to the console. The console then interprets this signal and takes the appropriate action in the game. Similarly, when you turn the volume knob on your stereo, it adjusts the resistance in a circuit, which in turn changes the amplitude of the audio signal.
More sophisticated controllers may use microprocessors to process input and generate more complex control signals. These microprocessors can be programmed to perform a wide range of functions, such as filtering noise, calibrating sensors, and implementing control algorithms. This is particularly common in industrial controllers, where precise and reliable control is essential.
Wireless controllers add another layer of complexity. These devices use radio waves, infrared light, or Bluetooth technology to communicate with the controlled system. They need to encode the control signals into a format that can be transmitted wirelessly, and the system needs to decode these signals and take the appropriate action. It's a bit like sending a secret message across the room!
Why Controllers Matter
4. The Significance of Controllers in Everyday Systems and Technologies
It's easy to take controllers for granted. We use them so often that we barely even think about them. But the truth is, controllers play a crucial role in shaping our modern world. They allow us to interact with technology in a natural and intuitive way. Without controllers, many of the devices and systems we rely on every day would be simply unusable.
Consider the impact of controllers on gaming. They've transformed gaming from a niche hobby into a global phenomenon. The evolution of game controllers has enabled increasingly immersive and complex gaming experiences. From simple arcade joysticks to sophisticated virtual reality controllers, these devices have pushed the boundaries of what's possible in the world of interactive entertainment.
In industry, controllers have revolutionized manufacturing processes. They've enabled automation, increased efficiency, and improved safety. PLCs and other industrial controllers are the unsung heroes of the modern factory, ensuring that products are made to exacting standards. They also make it possible to produce goods on a massive scale, driving down costs and making products more accessible to consumers.
Controllers are also essential for transportation. They allow us to safely and efficiently operate cars, airplanes, and other vehicles. The development of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), such as adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assist, relies heavily on sophisticated controllers that can monitor the environment and make real-time adjustments. As we move towards self-driving cars, controllers will become even more important.

Difference Between ONOFF Controller And PID
The Future of Control
5. Emerging Trends and Innovations in Controller Technology
So, what does the future hold for controllers? As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and sophisticated controllers emerge. One key trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance controller functionality. AI-powered controllers can learn from user behavior, adapt to changing conditions, and even anticipate user needs. Imagine a gaming controller that automatically adjusts its settings based on your playing style, or an industrial controller that can predict and prevent equipment failures.
Another exciting area of development is haptic feedback. Haptic controllers provide tactile sensations that simulate the feeling of interacting with virtual objects. This technology has the potential to revolutionize gaming, virtual reality, and even robotics. Imagine feeling the texture of a virtual object or the resistance of a virtual surface. This would add a whole new level of realism to these experiences.
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are also showing promise as a future control technology. BCIs allow users to control devices using their thoughts. While this technology is still in its early stages of development, it has the potential to transform the way we interact with computers and machines. Imagine controlling a prosthetic limb with your thoughts or playing a video game using only your mind. Okay, that sounds slightly terrifying, but also undeniably cool!
Finally, we can expect to see controllers become more integrated into our daily lives. Smart homes, wearable technology, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are all creating new opportunities for controllers to manage and automate our environment. Imagine a smart thermostat that learns your preferences and adjusts the temperature automatically, or a smart refrigerator that orders groceries when you're running low. The future of control is all about seamless integration and personalized experiences.
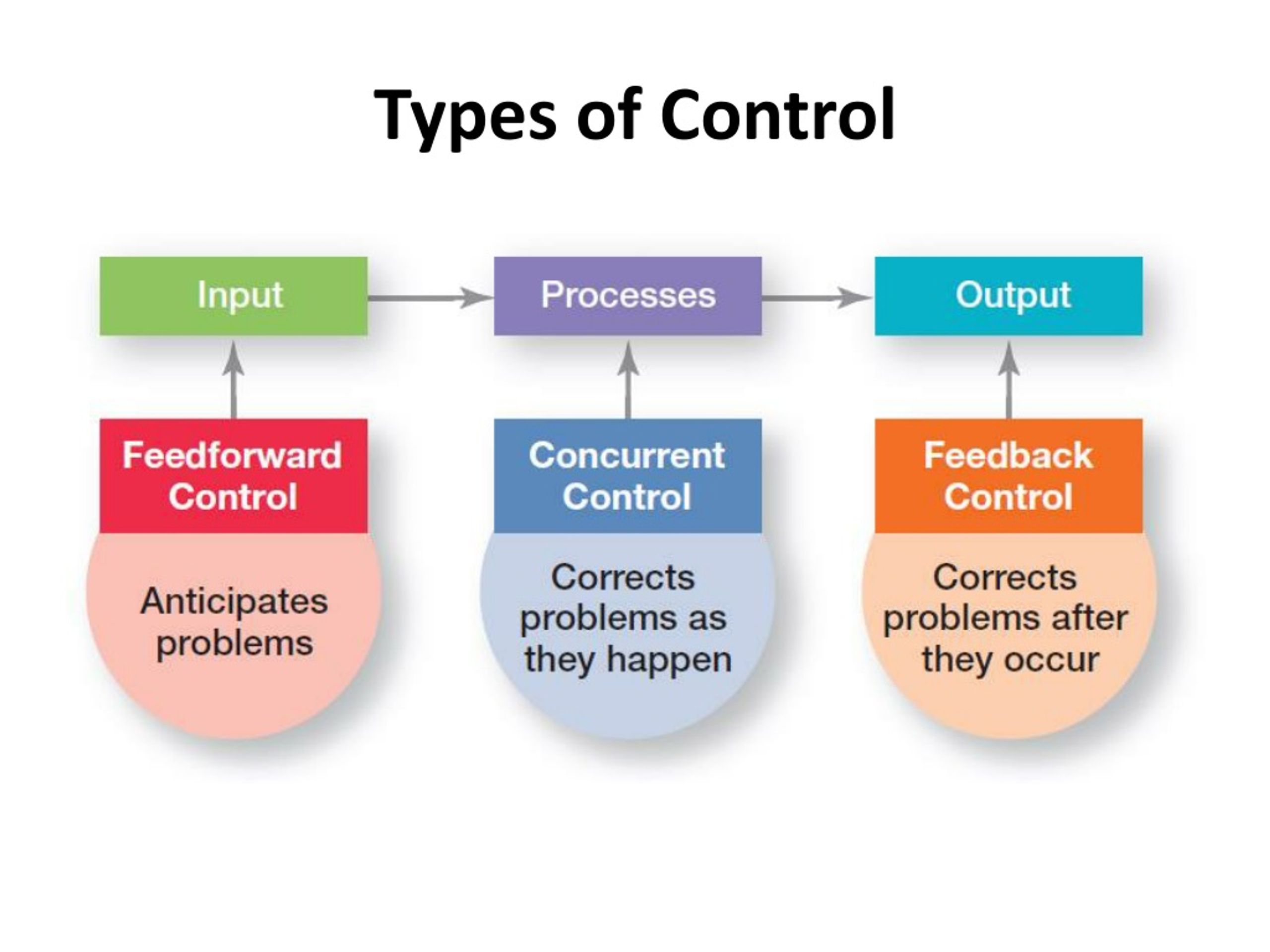
What Are The Different Types Of Controls At Ethan Fuhrman Blog
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
6. What's the difference between a controller and a remote control?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, a "controller" is a broader term. A remote control is a type of controller, specifically one used to operate a device from a distance, typically wirelessly. A controller can also be directly connected, like a steering wheel or a joystick, and may involve more complex interactions than simply on/off or channel up/down.
7. Are PLCs only used in factories?
Not at all! While Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are heavily used in manufacturing, their applications extend far beyond factory floors. You can find them controlling systems in power plants, water treatment facilities, traffic lights, and even amusement park rides. Any complex automated process can benefit from a PLC.
8. Will AI eventually replace all human controllers?
That's a complex question! While AI is certainly becoming more sophisticated and capable of automating many tasks, it's unlikely to completely replace human controllers in all situations. There will always be a need for human oversight, particularly in situations that require critical thinking, creativity, or adaptability. Think of AI as augmenting, rather than completely replacing, human controllers — at least for the foreseeable future. After all, who else will be around to blame when the robot vacuum starts attacking the cat?